Rhizopus stolonifer
 |
| Rhizopus diagram |
General characteristics
- R. stolonifer (Syn = R. nigricans) is commonly known as "Bread mold".
- Hyphae are aseptate and multinucleate.
- Hyphae grow horizontally to the substratum called "stolon".
- Branched rhizoids are produced at the point where stolon touches the substratum.
- Opposite to the rhizoids, aerial "sporangiophores" are born.
- Sporangiophores are long, unbranched and produced in umbell fashion.
- At the tip of sporangiophore, single terminal sporangium is produced.
- Sporangium is differentiated into lower sterile columella and upper fertile sporangial sac.
- Sporangiospores are born endogenously in the fertile sporangial sac.
- On maturity sporangial wall breaks into the fragments and columella hangs above the sporangiophores, this appears like an umbrella or inverted bowl.
- Spores are non-sticky and blown to a wider area in the air.
- Spores are non-motile (=aplanospores).
Economic importance
- R. stolonifer is a facultative parasite over mature fruits and vegetables.
- It is the source of
- Fumaric acid
- Lactic acid
- Cortisone (=steroid)
- Some species cause "mucoromycosis" in human.
- It is a common contaminant in microbial laboratories.
 |
| Rhizopus growing in habitat |
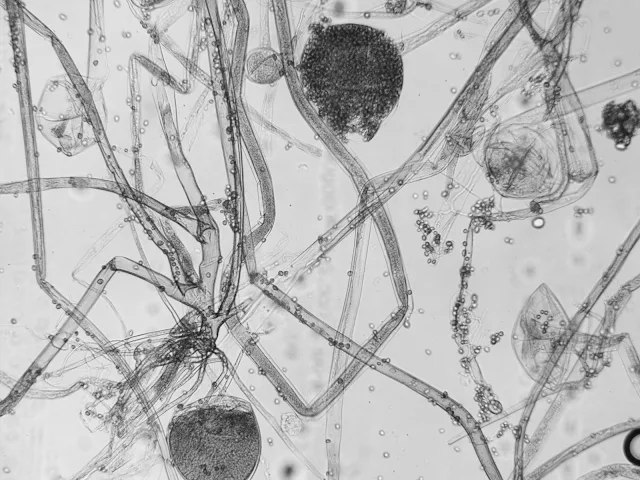 |
| Rhizopus stolonifer (Microscopic view) |
Content first created on 30-11-2022
last updated on 10-12-2022
last updated on 10-12-2022





5 Comments
Sir ye bhi file me note karna hai
ReplyDeleteYes
DeleteLove
ReplyDeleteThank You for your appriciation. Keep on growing.
DeleteSir isko file me note Krna hai
ReplyDeleteLeave your comments here.