Sphagnum
Classification
General characteristics
- Sphagnum is a genus of about 380 species moss.
- It is commonly known as peat moss or bog moss.
- Main plant body is gametophytic and differentiated into axis and leaves.
- The plants are perennial and grow in swamps and moist habitats.
- Plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight.
- Dead plant parts do not decompose easily because of the presence of phenolic compounds in the cell wall.
- Mature plants possess three types of branches- i) pendent branches, ii) divergent branches, and iii) coma branches.
- Plants do not have a vascular system.
- Leaves are single layered with two distinct types of cells.
- Small, green, living cells with chlorophyll (chlorophyllose cells) that produce food for the plant.
- Larger hyaline cells that are barrel shaped and have a pore at one end to allow for water absorption and improved water-holding capacity. These cells have spiral thickenings.
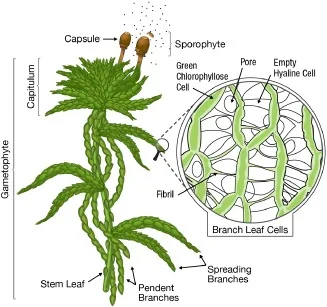 |
| Sphagnum: habit of plant body and whole mount (WM) of a leaf. (image source: ResearchGate) |
Uses
- Dried sphagnum (peat moss) is used in horticulture to enhance the water retaining capacity.
- These are used to make moss stick to grow other plants.
- Dried plants are used for dressing on the grafted part of the two plants.
- During World War I it was used in place of cotton in surgical dressing to heal the wounds.
- Because of the acidic nature, it is extremely resistant to degradation of bacteria and fungi and hence used in transportation of plant materials.
- Peat moss is used to grown orchids.
Content first created on 26-02-2024
last updated on 26-02-2024
last updated on 26-02-2024





0 Comments
Leave your comments here.